Informal settlements
In most African cities, more than half of residents live in informal settlements, with insecure tenure, a lack of basic services and infrastructure, and often unsafe housing. It is now widely recognised within policy and academic circles that such households tend to be best served by upgrading programmes that enable them to remain in situ, without disrupting their livelihoods and social networks.
Informal settlement upgrading is a significant poverty reduction mechanism, enabling low-income households to secure essential services at a lower cost, improve their social status, and overcome spatial inequality. It also helps address the needs of vulnerable groups, such as women-headed households and people with disabilities, as well as offering multiple opportunities for income generation.
City elites are increasingly recognising the potential that informal settlement upgrading has for enhancing their popularity. Our research closely analyses the politics underpinning such interventions. With multiple actors involved and a number of contentious issues shaping the challenge of upgrading, the complexities of the process and the overlaps with other urban development domains are a key focus in our work.
LATEST NEWS from ACRC

Empowering Mogadishu’s young people in civic activism and urban citizenship
Building on ACRC’s research in Mogadishu, the Heritage Institute for Policy Studies organised a three-day workshop on “Empowering youth for civic activism and urban citizenship”, in collaboration with ACRC and the Somali Gender and Equity Movement (SGEM).

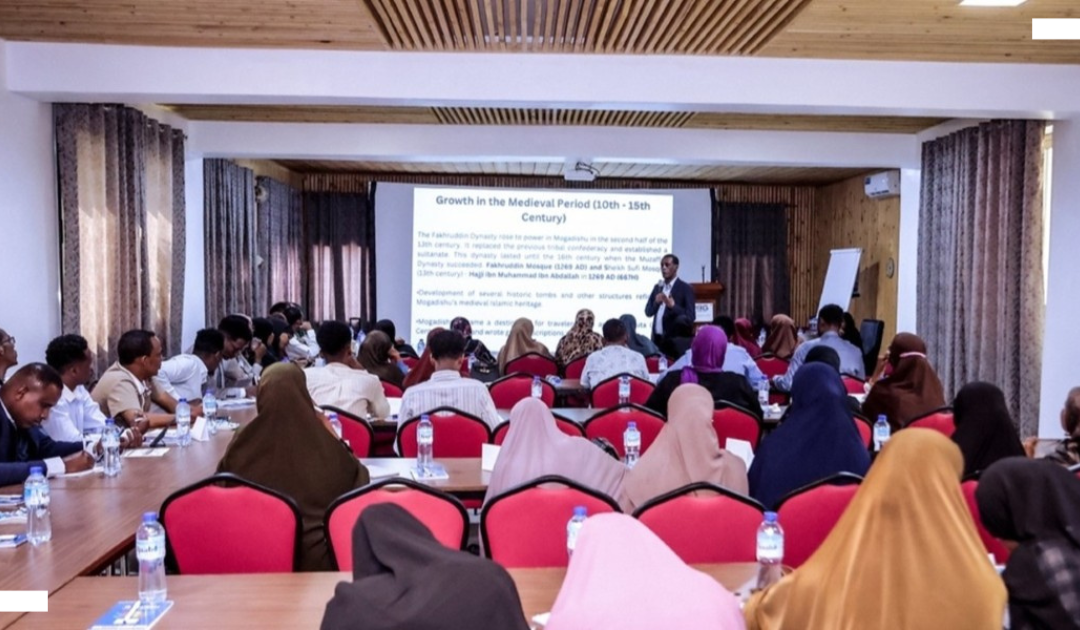
Watch: Water, sanitation and dignity in Mukuru Viwandani
A new video showcases the power of collaboration between government, civil society organisations, development partners and local communities in delivering transformative and inclusive water and sanitation services to marginalised residents of the Mukuru informal settlements in Nairobi.

Streetlights in Lagos can boost safety and grow the economy – why not everyone benefits
Streetlighting plays a crucial role in public safety and security, and it promotes inclusive social and economic development by boosting local commerce, street businesses and community engagement.