Neighbourhood and district economic development
The majority of African urban residents live and work in informal settlements, engaged in small-scale, often home-based economic activities. Earnings from these activities are typically low and precarious, with informal moneylenders providing vital services to residents, but usually on exploitative terms.
Some residents work beyond their neighbourhood, through their own microenterprises or employed by larger businesses, which tend to be more stable, regularised and with better established markets. However, due to unreliable infrastructure services and limited benefits of co-location in African cities, there are few such firms, so their contribution to poverty reduction and structural transformation is limited.
Looking through ACRC’s political economy lens, neighbourhood and district economic development reflects the distribution of economic and land rent in the local economy. City systems need to be mobilised so that enterprises can function smoothly. The living standards of the urban poor in these neighbourhoods could therefore be improved by strengthening city economies, generating “decent work” opportunities and boosting entrepreneurial skills. This involves a wide range of key actors, including economic development agencies, business/trade associations, informal business networks, trade unions and other labour organisations, and local politicians.
Within the neighbourhood and district economic development domain, we are focusing on the following cities:
LATEST NEWS from ACRC
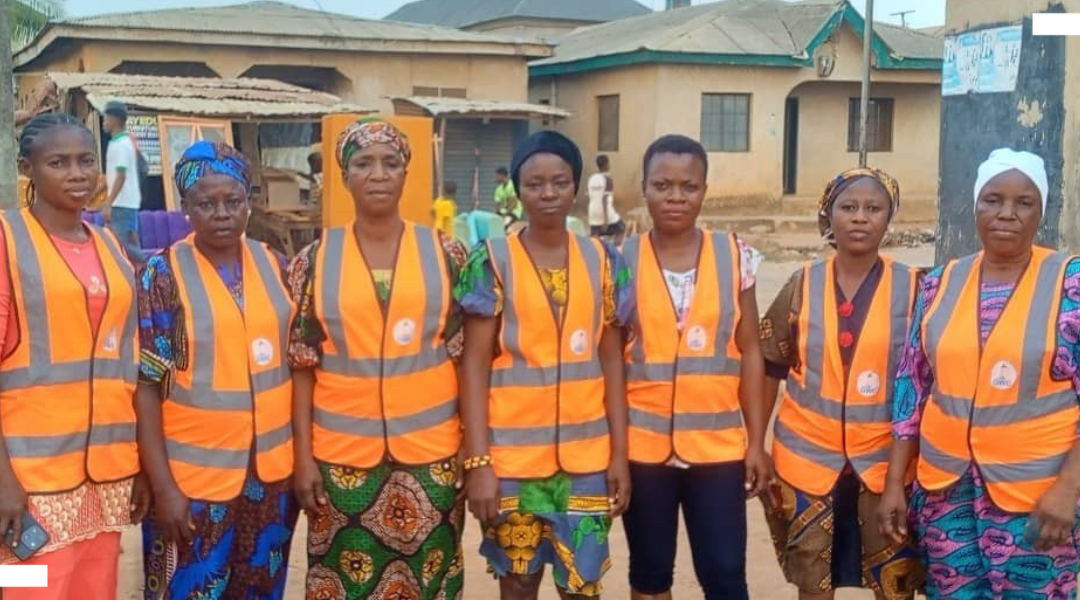

Transforming informal settlements in Lagos through community-driven WASH innovation: The Okerube project
The “Informal Settlements as Spaces of Transformative Agency” project focuses on the Okerube community in Lagos to challenge dominant narratives and demonstrate how bottom-up, community-led governance models can deliver sustainable and inclusive water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) solutions in informal urban settlements.

Creating the conditions for change in Mathare informal settlement, Nairobi
SDI Kenya, through ACRC, is aiming to co-develop solutions with Mathare community members, by devising a holistic waste management system in the area.

How does action research build community and state capabilities?
This is the fourth in a series of blog posts focusing on how urban reform happens, and where ACRC fits into change processes. This post takes a closer look at how ACRC is helping build community capabilities to address urban challenges.